Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Welcome to the Pulsar Vertex corporate security guide! As a seasoned security professional with 20 years of industry experience, I’m excited to share my expertise on corporate security, perimeter detection, and access control systems. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of protecting warehouses and large-scale industrial facilities. Our goal? To provide you with detailed, informative, and actionable insights that enhance your security strategy.
1. Understanding Corporate Security
The Role of Corporate Security
Corporate security extends beyond physical protection. It encompasses information security, risk management, and business continuity. As a corporation, your assets include not only tangible goods but also intellectual property, customer data, and brand reputation.
Threat Landscape: Challenges Faced by Corporations

- Cyber Threats: Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and insider threats.
- Physical Threats: Theft, vandalism, and unauthorized access.
- Supply Chain Risks: Vulnerabilities in the global supply chain.
Holistic Security Approach: Beyond Physical Measures
Effective corporate security integrates technology, policies, and personnel. Consider:
- Security Culture: Fostering awareness and vigilance among employees.
- Incident Response Plans: Swift action during emergencies.
- Collaboration with Law Enforcement: Reporting and investigations.
2. Perimeter Detection Systems
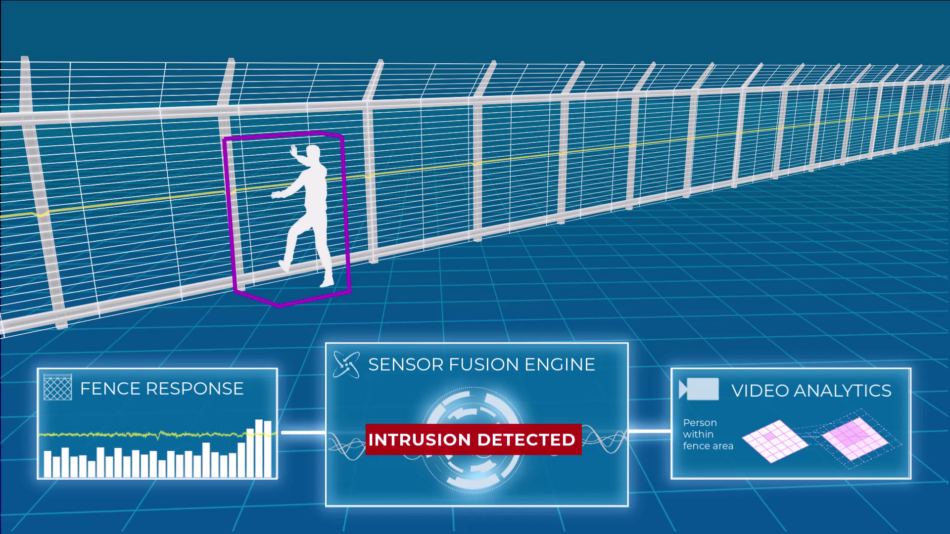
Types of Perimeter Sensors
- Infrared Sensors: Detecting motion with anti-masking features
- Ideal for night surveillance.
- Differentiating between humans, animals, and vehicles.
- Microwave Sensors: Monitoring Movement created by heat
- Wide coverage area.
- Immune to weather conditions.
- Fiber Optic and microphonic Sensors: Precise Vibration Detection
- Detects fence tampering or climbing attempts.
- CCTV with AI and smart analytics.
If you need more detailed information about types of perimeter security systems , click here !
Integration with CCTV: Real-Time Alerts
- Video Analytics: Combining perimeter sensors with CCTV.
- Automated Alerts: Intrusion notifications to security personnel.
- Evidence Collection: Crucial for investigations.
3. Access Control Solutions
Key Cards and Biometrics
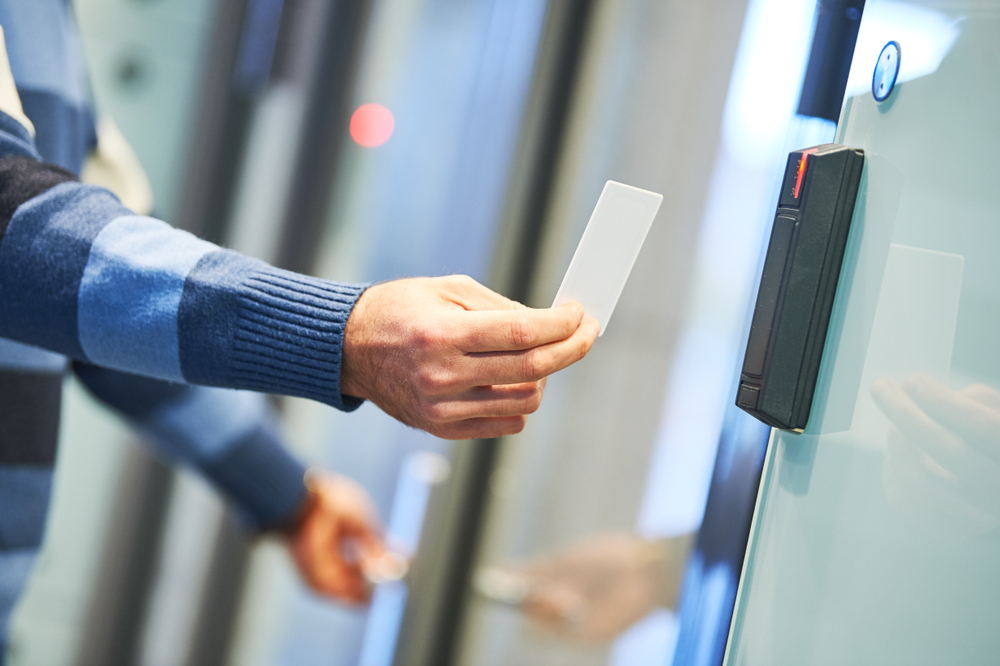

Key Cards: Convenient and customizable access.
Key card door entry systems offer customizable access levels, replacing traditional lock-and-key mechanisms. Employees swipe cards for efficient building entry, enhancing security and productivity
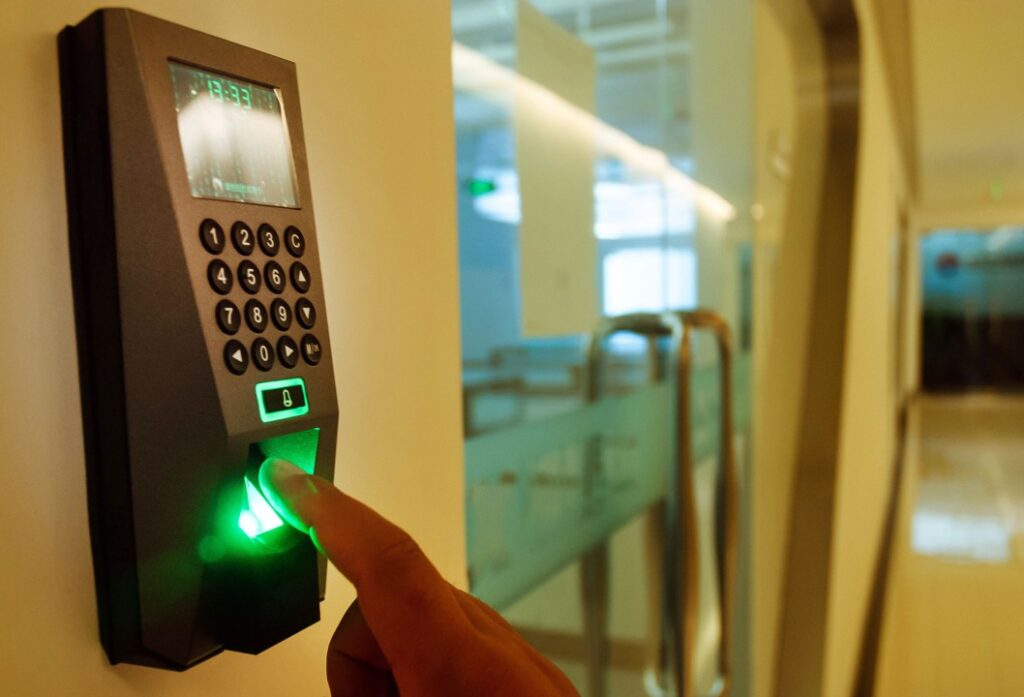

Biometrics: Unique identifiers (fingerprint, retina, etc.).
Biometric access control systems use unique physiological features (like fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans) to verify identity and grant secure area access. Enhanced security, ease of use, and non-transferability are key benefits
PIN Codes and Smart Cards
- PIN Codes: Simple yet effective.
- Smart Cards via NFC and cloud access : Encrypted data for secure access.
Two-Factor Authentication
- Layered Security: Combining two authentication methods.
- Mobile Apps and Tokens: Enhancing user experience.
4. Warehouse-Specific Considerations
Layout Optimization
Zoning: Segregating high-risk areas (e.g., server rooms).
Zoning in access control design involves segmenting an organization’s network into smaller, controlled areas. For instance, segregating high-risk zones like server rooms from the rest of the network enhances security and limits potential intrusions.
Asset Tracking Systems
- RFID Tags: Real-time location tracking.
Unlocking Efficiency: RFID Tags for Real-Time Location Tracking in Logistics and Factories
In the dynamic world of logistics and manufacturing, precision and visibility are paramount. Enter Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology—a game-changer that empowers businesses to track goods seamlessly and optimize operations. Let’s explore how RFID tags serve as an additional layer of security while enhancing efficiency.
- Enhanced Authentication and Anti-Counterfeiting Measures:
- Secure Communication: RFID tags transmit data wirelessly, enabling real-time tracking. Implement robust encryption and authentication protocols to safeguard sensitive information.
- Unique Identifiers: Each RFID tag carries a distinct identifier, making it virtually impossible to clone or tamper with. This authenticity layer prevents counterfeiting and ensures supply chain integrity.
- Access Control and Asset Protection:
- Access Points: Strategically position RFID readers at critical points—entrances, loading docks, and bottlenecks. Authenticate personnel, vehicles, and goods as they move through the facility.
- Asset Tracking: Monitor high-value assets (such as machinery, tools, or sensitive materials) using RFID tags. Instantly detect any unauthorized movement or removal.
- Supply Chain Transparency:
- End-to-End Visibility: RFID tags enable granular tracking from factory floor to final delivery. Know where each item is at all times, minimizing delays and ensuring timely shipments.
- Inventory Management: Accurate inventory counts lead to efficient restocking, reduced stockouts, and optimized storage space. RFID automates this process, reducing manual errors.
- Operational Streamlining:
- Automated Workflows: RFID streamlines processes. As goods pass RFID-enabled checkpoints, data updates automatically. This minimizes paperwork, accelerates order fulfillment, and enhances overall productivity.
- Predictive Insights: Analyze historical RFID data to identify patterns, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. Make informed decisions to optimize workflows.
- Challenges and Mitigation:
- Security: While RFID enhances efficiency, it also introduces security risks. Protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and tag cloning.
- Privacy: Balance real-time tracking with privacy concerns. Anonymize data where needed and comply with regulations.
In summary, RFID tags are more than mere identifiers—they’re the linchpin of modern logistics and factory management. By embracing this technology and implementing robust security practices, businesses can unlock efficiency, bolster security, and stay ahead in the competitive landscape.
- GPS Technologies: Outdoor asset monitoring.
Certainly! Let’s delve into the world of GPS asset tracking—a powerful technology that leverages the Global Positioning System (GPS) to monitor assets in real time. Whether it’s vehicles, equipment, or personal valuables, GPS tracking provides efficiency and security. Here’s a guide to maximizing its benefits:
- Understanding GPS Asset Tracking:
- What Is It?: GPS asset tracking involves using satellite-based GPS technology to precisely locate and monitor assets outdoors.
- Applications: It’s widely used across various domains, including logistics, transportation, and agriculture.
- Real-Time Insights: By tracking assets’ movement and status, businesses gain actionable insights for better decision-making.
- Key Benefits:
- Location Accuracy: GPS provides precise latitude and longitude coordinates, enabling accurate asset positioning.
- Real-Time Updates: Monitor assets remotely, ensuring timely responses to any deviations or incidents.
- Cost Savings: Efficient asset management reduces losses, prevents theft, and optimizes resource allocation.
- Enhanced Security: Quickly recover stolen assets or respond to emergencies.
- Ideal Use Cases:
- Fleet Management: Real-time tracking of vehicles (trucks, delivery vans, etc.) ensures efficient routes, driver safety, and on-time deliveries.
- Construction Equipment: Monitor heavy machinery, cranes, and excavators on job sites.
- Agricultural Assets: Track tractors, combines, and other farm equipment.
- High-Value Goods: Protect valuable cargo during transportation.
- Personal Assets: Use GPS trackers for pets, luggage, or outdoor adventures.
- Limitations and Solutions:
- Signal Interference: GPS signals can weaken in urban canyons or dense forests. Consider hybrid solutions (e.g., combining GPS with cellular or Wi-Fi).
- Battery Life: Some GPS devices consume power. Opt for energy-efficient models or solar-powered options.
- Indoor Coverage: GPS primarily works outdoors. For indoor tracking, explore Wi-Fi or Bluetooth-based solutions.
- New Frontiers:
- Low-Power GPS: Emerging technologies reduce energy consumption, extending battery life for long-term tracking.
- Edge Computing: Process data locally on the device, minimizing reliance on cloud services.
- Geofencing: Set virtual boundaries and receive alerts when assets cross predefined zones.
In summary, GPS asset tracking empowers businesses to optimize operations, enhance security, and stay ahead in a dynamic world.
Security Guards
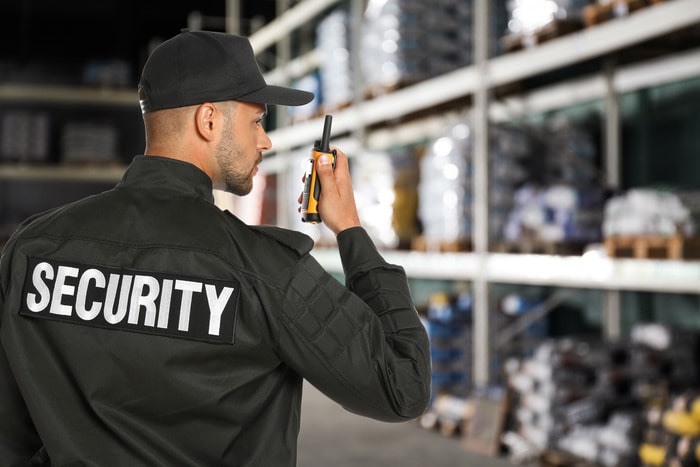

- Human Surveillance: Visual deterrence and incident response.
- Training: Security personnel as first responders.
Lighting and Fencing
- Illumination: Well-lit perimeters discourage intruders.
- Fencing: Physical barrier with access control points.
5. Alarm Systems for Large-Scale Facilities

Advanced Perimeter Security
- Thermal Imaging Sensors: These sensors detect heat signatures, making them effective even in low-light conditions. By identifying temperature variations, they can alert security personnel to potential intruders.
- Vibration Sensors: Installed on fences and walls, these sensors detect any attempts to breach the perimeter. They are sensitive to vibrations caused by cutting tools or climbing.
- Laser-Based Systems: Utilizing laser beams, these systems create an invisible barrier. If the beam is interrupted, an alarm is triggered. They are particularly useful for open areas.
Integration with CCTV and Access Control
- CCTV Integration: When perimeter sensors detect an intrusion, they trigger nearby CCTV cameras to focus on the affected area. This provides real-time visual confirmation and aids in assessing the situation.
- Access Control Synergy: Integrating access control systems with perimeter security ensures that only authorized personnel can enter specific zones. Access logs can be cross-referenced with perimeter breach alerts.
Emergency Protocols
- Drills and Preparedness: Regular emergency drills are essential. Security personnel should know how to respond to alarms, coordinate with law enforcement, and guide employees during evacuations.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the multifaceted world of corporate security, perimeter detection, and access control. Remember that security is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Tailor your approach to the unique needs of your warehouse or industrial facility. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and safeguard your assets with the latest technologies and best practices.
Thank you for joining us at Pulsar Vertex. If you have any further questions or need personalized advice, feel free to reach out. Stay secure! 🔒

